How to Calculate LLM Model Parameter Size - MoE Model
This guide explains how to calculate the parameter size of a Mixture of Experts (MoE) large language model (LLM) using its architecture and configuration file. We’ll use the Qwen3-30B-A3B model as an example to demonstrate the process.
1. Understand the Model Architecture
To calculate a model’s parameter size, you first need to understand its architecture. Initially, I considered technical reports as a primary source, but for models like Qwen3, which inherit the Llama architecture, these reports may lack detailed implementation specifics. Instead, reviewing the model’s code in popular repositories provides deeper insight.
For MoE Model architecuture, we can refer to the
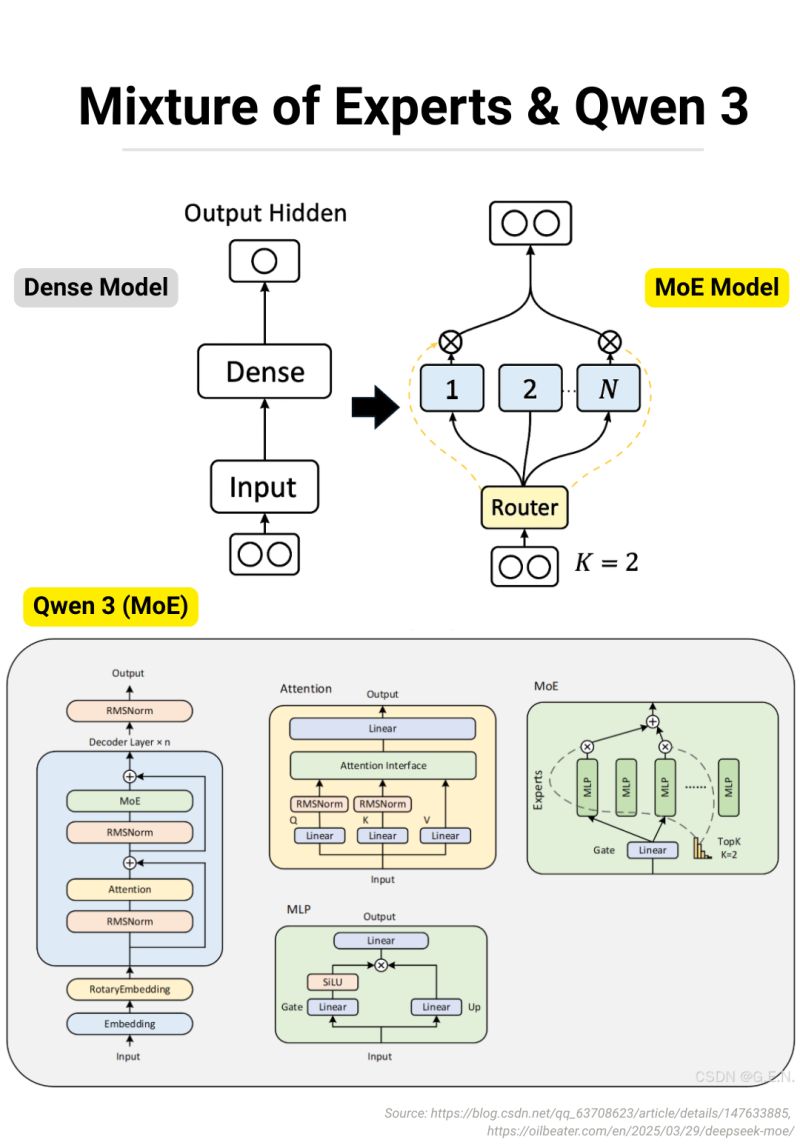
For Qwen3 MoE detailed implementation, which follows the Llama MoE architecture, you can refer to the following implementations:
- Huggingface Qwen3 MoE Model Implementation: Link
- SGLang Qwen3 MoE Model Implementation: Link
- vLLM Qwen3 MoE Model Implementation: Link
2. Extract Key Parameters from config.json
The model’s config.json file, available on the Qwen3-30B-A3B Hugging Face model card, contains critical parameters for calculating the model’s size.
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
vocab_size | 151936 | Size of the vocabulary |
hidden_size | 2048 | Hidden dimension size |
num_hidden_layers | 48 | Number of transformer layers |
num_attention_heads | 32 | Number of attention heads |
num_key_value_heads | 4 | Number of key-value heads (for GQA) |
moe_intermediate_size | 768 | Size of MoE MLP component |
num_experts | 128 | Number of experts |
head_dim | 128 | Dimension of each attention head |
3. Calculate the model Parameter Size
Using the MoE-based architecture and the parameters from config.json, we can compute the total number of parameters in Qwen3-30B-A3B. The model consists of an embedding layer, transformer layers (with self-attention and multiple MoE MLP components), and a language model head. Below is the breakdown:
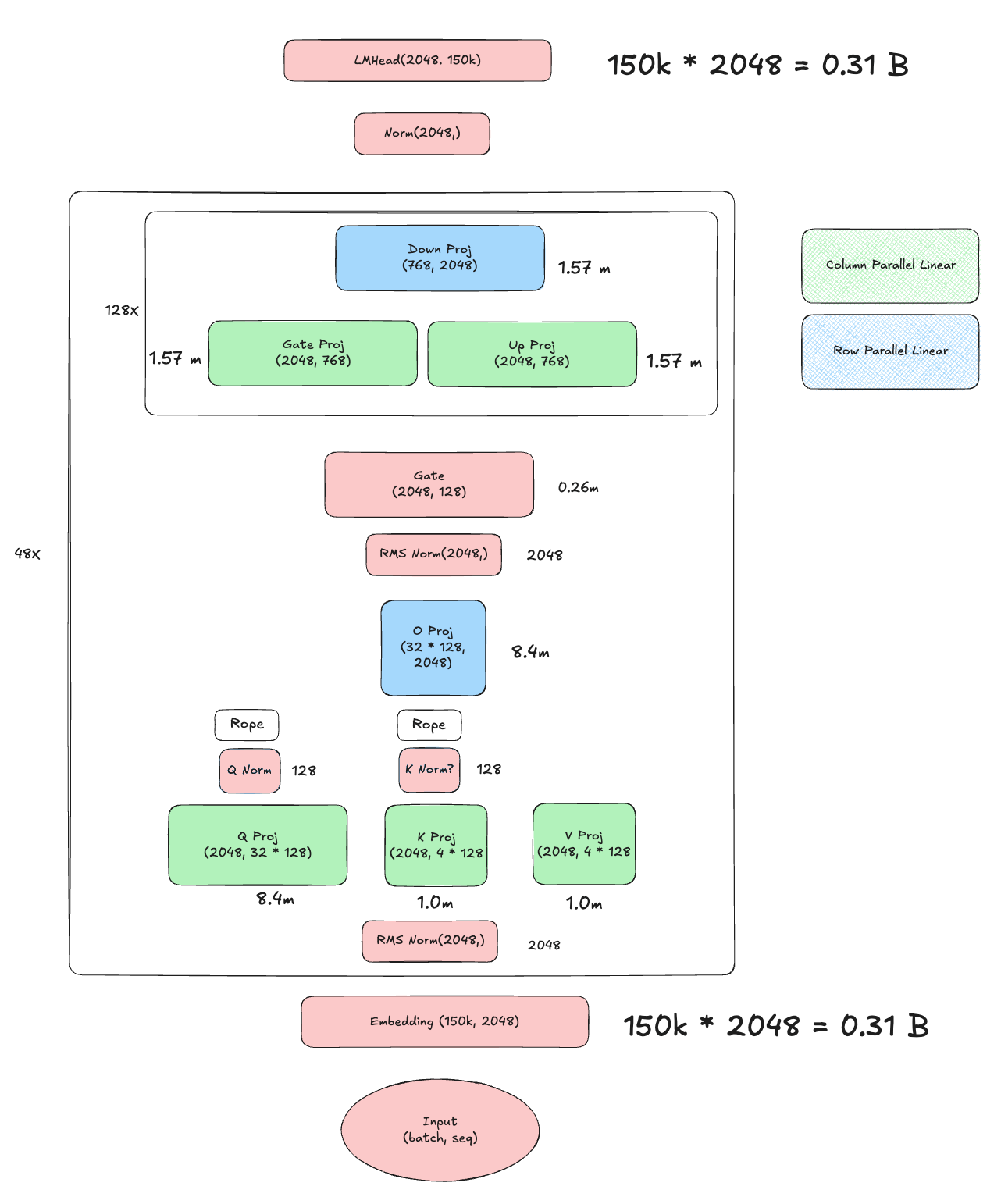
- Embedding Layer
- Parameters:
vocab_size × hidden_size - Calculation:
151936 × 2048 = 311,164,928 ≈ 0.31B
- Parameters:
-
Transformer Layers (48 × Qwen3MoeDecoderLayer)
Each of the 48 transformer layers includes self-attention and 128 MoE MLP components, with layer normalization parameters (which are negligible in size).
- Self-Attention (18.8M per layer)
- Q Projection:
hidden_size × (num_attention_heads × head_dim)2048 × (32 × 128) = 2048 × 4096 = 8,388,608 ≈ 8.4M
- K Projection:
hidden_size × (num_key_value_heads × head_dim)2048 × (4 × 128) = 2048 × 512 = 1,048,576 ≈ 1.0M
- V Projection:
hidden_size × (num_key_value_heads × head_dim)2048 × (4 × 128) = 1,048,576 ≈ 1.0M
- O Projection:
(num_attention_heads × head_dim) × hidden_size(32 × 128) × 2048 = 4096 × 2048 = 8,388,608 ≈ 8.4M
- Q/K Norms:
head_dim = 128(negligible, ignored) - Total per layer:
8.4M + 1.0M + 1.0M + 8.4M = 18.8M - Across 48 layers:
18.8M × 48 = 902.4M
- Q Projection:
- MoE (393M per layer)
- MoE Gate:
hidden_size × num_experts2048 × 128 = 262,144 ≈ 0.26M
- MoE MLP
- Gate Projection:
hidden_size × moe_intermediate_size2048 × 768 = 1,572,864 ≈ 1.57M
- Up Projection:
hidden_size × moe_intermediate_size2048 × 768 = 1,572,864 ≈ 1.57M
- Down Projection:
moe_intermediate_size x hidden_size768 x 2048 = 1,572,864 ≈ 1.57M
- Total per expert:
1.57M + 1.57M + 1.57M = 4.71M - Across 128 experts:
4.71M × 128 = 602.88M
- Gate Projection:
- Total per layer:
0.26M + 602.88M = 603.14M - Across 48 layers:
603.14M × 48 = 28,950.72M ≈ 28.95B
- MoE Gate:
- Layer Norms:
hidden_size = 2048per norm (input and post-attention, negligible, ignored) - Total per layer:
18.8M + 603.14M = 621.94M - Across 48 layers:
621.94M × 48 = 29,853.12M ≈ 29.85B
- Self-Attention (18.8M per layer)
- Output Layer Norm
- Parameters:
hidden_size = 2048(negligible, ignored)
- Parameters:
- Language Model Head
- Parameters:
hidden_size × vocab_size - Calculation:
2048 × 151936 = 311,164,928 ≈ 0.31B
- Parameters:
Total Parameters:
0.31B (Embedding) + 29.85B (Transformer Layers) + 0.31B (LM Head) ≈ 30.47B
4. Verify the Calculation
The Qwen3-32B-A3B model card reports a total parameter count of 32.5B, with non-embedding parameters totaling 29.9B. These figures align closely with our calculations, confirming their accuracy.

5. Programatic Calculation
To automate the parameter calculation, you can use a Python script with the Hugging Face transformers library. The script below loads the Qwen3-32B-A3B model and tallies parameters by component:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
import torch
from collections import defaultdict
import re
model_path = "/shared/public/elr-models/Qwen/Qwen3-30B-A3B/67b0e0ca24de1b8cedea4c97f1925df66d72bee1"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_path,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
device_map="auto",
trust_remote_code=True
)
print(model)
# Dictionary to store parameter counts per submodule
param_groups = defaultdict(int)
# Traverse all named parameters
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
if not param.requires_grad:
continue
if "embed_tokens" in name:
param_groups["Embedding"] += param.numel()
elif "lm_head" in name:
param_groups["LM Head"] += param.numel()
elif ".self_attn.q_proj" in name:
param_groups["Attention/q_proj"] += param.numel()
elif ".self_attn.k_proj" in name:
param_groups["Attention/k_proj"] += param.numel()
elif ".self_attn.v_proj" in name:
param_groups["Attention/v_proj"] += param.numel()
elif ".self_attn.o_proj" in name:
param_groups["Attention/o_proj"] += param.numel()
elif ".self_attn.q_norm" in name:
param_groups["Attention/q_norm"] += param.numel()
elif ".self_attn.k_norm" in name:
param_groups["Attention/k_norm"] += param.numel()
elif ".mlp.gate_proj" in name:
param_groups["MLP/gate_proj"] += param.numel()
elif ".mlp.up_proj" in name:
param_groups["MLP/up_proj"] += param.numel()
elif ".mlp.down_proj" in name:
param_groups["MLP/down_proj"] += param.numel()
elif ".mlp.gate" in name:
param_groups["MLP/gate"] += param.numel()
elif re.search(r"\.experts\.\d+\.gate_proj", name):
param_groups["MLP/experts/gate_proj"] += param.numel()
elif re.search(r"\.experts\.\d+\.up_proj", name):
param_groups["MLP/experts/up_proj"] += param.numel()
elif re.search(r"\.experts\.\d+\.down_proj", name):
param_groups["MLP/experts/down_proj"] += param.numel()
elif "input_layernorm" in name:
param_groups["LayerNorm/input"] += param.numel()
elif "post_attention_layernorm" in name:
param_groups["LayerNorm/post_attention"] += param.numel()
elif name.startswith("model.norm"):
param_groups["LayerNorm/final"] += param.numel()
elif "rotary_emb" in name:
param_groups["RotaryEmbedding"] += param.numel()
else:
param_groups["Other"] += param.numel()
total_params = sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters())
print(f"Total params: {total_params / 1e9:.2f}B")
total_params_calculated = sum(v for k,v in param_groups.items() if k != 'Other')
print(f"Total params calculated: {total_params_calculated / 1e9:.2f}B")
Sample Output
Qwen3MoeForCausalLM(
(model): Qwen3MoeModel(
(embed_tokens): Embedding(151936, 2048)
(layers): ModuleList(
(0-47): 48 x Qwen3MoeDecoderLayer(
(self_attn): Qwen3MoeAttention(
(q_proj): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=4096, bias=False)
(k_proj): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=False)
(v_proj): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=False)
(o_proj): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=2048, bias=False)
(q_norm): Qwen3MoeRMSNorm((128,), eps=1e-06)
(k_norm): Qwen3MoeRMSNorm((128,), eps=1e-06)
)
(mlp): Qwen3MoeSparseMoeBlock(
(gate): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=128, bias=False)
(experts): ModuleList(
(0-127): 128 x Qwen3MoeMLP(
(gate_proj): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=768, bias=False)
(up_proj): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=768, bias=False)
(down_proj): Linear(in_features=768, out_features=2048, bias=False)
(act_fn): SiLU()
)
)
)
(input_layernorm): Qwen3MoeRMSNorm((2048,), eps=1e-06)
(post_attention_layernorm): Qwen3MoeRMSNorm((2048,), eps=1e-06)
)
)
(norm): Qwen3MoeRMSNorm((2048,), eps=1e-06)
(rotary_emb): Qwen3MoeRotaryEmbedding()
)
(lm_head): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=151936, bias=False)
)
Embedding : 311.16M params
Attention/q_proj : 402.65M params
Attention/k_proj : 50.33M params
Attention/v_proj : 50.33M params
Attention/o_proj : 402.65M params
Attention/q_norm : 0.01M params
Attention/k_norm : 0.01M params
MLP/gate : 12.58M params
MLP/experts/gate_proj : 9663.68M params
MLP/experts/up_proj : 9663.68M params
MLP/experts/down_proj : 9663.68M params
LayerNorm/input : 0.10M params
LayerNorm/post_attention : 0.10M params
LayerNorm/final : 0.00M params
LM Head : 311.16M params
Total params: 30.53B
The programmatic results match the manual calculation, reinforcing confidence in the approach.
6. Conclusion
This guide demonstrated how to calculate the parameter size of a MoE LLM like Qwen3-32B-A3B using its architecture and config.json file. By breaking down the model into its components—embedding layer, transformer layers, and language model head—we computed a total of approximately 32.47 billion parameters, consistent with the official model card. Additionally, a Python script was provided to automate this process, offering a reusable tool for analyzing other models.
This approach can be applied to any transformer-based model by adapting the architecture-specific calculations and configuration parameters.